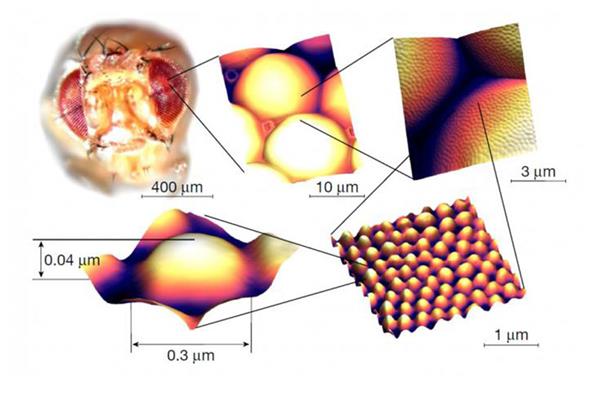
Scientists from Russia and Switzerland have developed a biodegradable nanocoating with antimicrobial and anti-reflective properties by studying the nanostructures covering the corneas of the eyes of small fruit flies.
Scientists from Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU, Russia) and from University of Geneva, The University of Lausanne, and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich teamed up to conduct an interdisciplinary research project during which they were able to artificially reproduce the nanocoating of the corneas of fruit flies (Drosophila flies) naturally designed to protect the eyes of the insects from dust particles and shut off the reflection of light.
By investigating these flies, the team learned how to produce a biodegradable nanocoating with antimicrobial, anti-reflective, and self-cleaning properties in a cost-effective and eco-friendly way.
How the study was conducted
Scientists managed to
rebuild the corneal coating of small fruit flies via direct and reverse
bioengineering methods. First, they took the protective layer apart into its constituent components, which turned out to be retinin (protein) and corneal wax (lipids), and then reassemble it under room temperature conditions, covering glass and plastic surfaces.
According to Vladimir Katanaev - the head of the research and Head of the Laboratory of Pharmacology of Natural Compounds in the School of Biomedicine of FEFU - any other types of materials can be nanocoated too. Combinations with different types of wax and genetic manipulations of the retinin protein allow the design of highly diverse and complex functional nanocoatings.
The scientist explains that the mechanism underlying the formation of the protective nanostructures on the corneas of Drosophila flies is a self-organizing process, described by Alan Turing back in 1952 as a reaction-diffusion mechanism. That is consistent with the mathematical modelling performed during the research. This mechanism is also responsible for the patterns forming, for example, on the fur of a zebra or a leopard. The nanostructures that protect the corneas of Drosophila eyes are the first established example of Turing patterns at the nanoscale.
In the course of the research project, scientists made a detailed characterization of the properties of retinin, as this protein has been little studied so far. It turned out that this initially unstructured protein forms a globular structure when interacting with corneal waxes. Thus, scientists took a look deep into the biophysical nature of the self-organization abiding to the Turing model, highlighting an important molecular process likely at the core of the self-organization: the initiation of the protein structuring.
Fields of application of the new nanocoating
This coating might
find applications in diverse areas of economics including medicine, nanoelectronics, automotive industry, and textile industry.
It can wrap up any flat or three-dimensional structure, and, depending on the task, give it anti-reflective, antibacterial, and hydrophobic properties, including self-cleaning.
The self-cleaning property, for example, is a very important feature for expensive reusable overnight ortho-k lenses that correct the eyesight. Similar anti-reflective coatings - which are being used on the panels of computers, glasses, painting in museums - are created by more complex and costly methods.
"We are able to produce the nanocoating in any required quantity given that its design is more cost-effective compared to the modern methods of manufacturing similar structures. The work with natural components requires no special equipment nor significant energy consumption and constraints of chemical etching, lithography, and laser printing," explains Vladimir Katanaev. "The development has broad applications. For example, it could be the structural dying of textiles that would change the colour depending on the angle of view. It is possible to create a disguise coat based on metamaterials, an antibacterial layer for medical implants, and a self-cleaning coating for contact lenses and windshields. We also believe that if we reinforce the nanocoating, it might be utilized as a basis of flexible miniature transistors prototypes designed for modern electronics."
What comes next?
Professor Vladimir Katanaev started studying the structure of the eye of Drosophila fly about 10 years ago.
According to the scientist, the first data were obtained almost impromptu by means of atomic force microscopy. During collaboration with the laboratory of Prof. Igor Serdyuk from the Institute of Protein Research (Russian Academy of Sciences), it was discovered that the surface of the corneas of the flies was not smooth but was covered with beautiful patterns of pseudo-ordered nanoscale outgrowths. As it turned out, nanocoatings of this kind were described back in the late 1960s on the surface of the eyes of moths, larger insects to whom these structures also provide an anti-reflex function, reducing the reflection of incident light to zero and allowing to optimize light perception in the darkness.
At next stages, the research team aims at developing a model of three-dimensional nanostructuring (with nano-funnels, nanocolumns, nanorolls within the layer of the coating), also based on the Turing mechanism. This work would lie at the very frontier of modern scientific knowledge and can have promising fundamental and technological consequences.
The study by professor Vladimir Katanaev and his team was published on the journal Nature.